Validation¶
Validation is very important and is mainly accomplished via Hooks: on_validation and on_field_validation__field_name are expressly created for that with all the variants for related tables.
There are many different snippets in the demo related to validation and hooks: they are part of the documentation.
Validation Errors¶
The validation has the following steps:
Each field in gui_fields, i.e. all fields that have a graphical representation are looked for the value and a hook named on_field_validation__field_name -if present- is run .
Note
At present fields representing m2m or o2m relations (e.g. movies in a director class) are not searched for on_field_validation__field_name hook. You can use on_validation hook to set validation on relations
Each method of the hooks class can raise a ValidationWarning directly that is caught by the main validation loop, and populates validation_error dict or can feed this dict via the sqlwidget’s method add_validation_error or add_not_null_error
This operation is repeated for each related process and the main validation_error dict is updated.
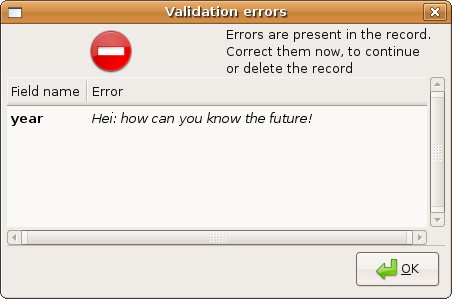
If the validation_error dict has collected some errors a ValidationErrorDialog is presented to the user:
class Hooks(object): def on_field_validation__year(self, mask, field_name, field_value, field): if field_value > 2020: raise ValidationError("Hey: how can you know the future!") t = SqlMask(model.Movie, layout=lay, label_map={'genres.name':'genres'}, dbproxy=db, hooks=Hooks())
that would raise a ValidationDialog as follows:
Validation Warnings¶
In a similar way you can raise/add a Validation Warning that will warn with a message but will not abort the process.
ValidationWarningDialog is presented after ValidationErrorDialog if both are needed.

